Technical
Technical Process
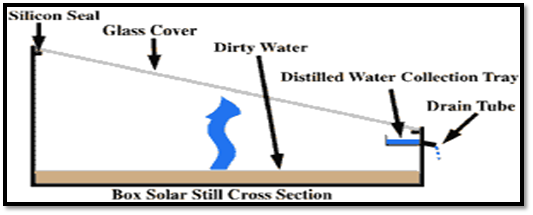
Solar distillation stills use heat from the sun to clean water. Commonly, a solar still consists of a shallow basin with a transparent glass cover. The sun heats water in the basin and causes the water to evaporate. The evaporated water rises until it hits the glass cover where it turns back to liquid and runs down the glass until it falls into the collection trough leaving the salts, minerals and bacteria in the basin. One example is a box solar still which can be seen in Figure 1.
Cover Structure
The purpose of this project is to develop new versions of solar distillation stills and document their performances based on the efficiency of purifying brackish groundwater without the addition of electricity. Through the use of solar distillation, we can use heat from the sun to evaporate potable water from the brackish water. The goal of this project is to design a still with the highest possible water production per unit cost of the process equipment.
Cover Material
Since incoming radiation is used to heat the water, a cover with low absorbing and reflecting properties will be used. A smooth transparent material is ideal for cover purposes. The smoothness decreases the amount of light that will be reflected, and can be utilized to collect condensation from inside the system. Unidirectional heat transfer material reduces heat loss making it an ideal choice for cover material.
Base
The base of the solar distillation still needs to provide the largest evaporation area possible. A large area will improve the efficiency of water treatment by increasing the evaporation rate. The ideal building material for the base of a solar distillation still is either copper or iron metal surrounded by insulating material. The copper or iron metal absorbs the heat and transfers it so the water can evaporate. The insulation helps to minimize the amount of heat loss. The efficiency of the system increases by lowering the heat loss and focusing the heat on a centralized location.
Challenges
There are several potential challenges for the creation of a solar distillation still. These challenges are listed below:
- Cost - Providing a low cost product at a high efficiency will allow the final design to be easily replicated and maintained.
- Electricity - Without an outside source of electricity, other means will be utilized to heat and pump the water throughout the system.
- Location’s water - The water presented at the competition may be different than the water presented at the test site.
- Efficiency - Theoretical water production efficiency may differ from actual efficiency of the still, resulting in lower production of water.
- Weather - Due to inconsistent weather conditions, it will be difficult to have ideal heating conditions for distilling the water.
Key Factors
The key factors for success concerning the improvement of the solar distillation still are listed below:
- Materials - Considerations for system performance, as well as material availability and durability at the selected location are essential for project success.
- Unit Construction and Maintenance - Ease of both unit set up and maintenance play an important role in project success.
- Production Rate - The highest production rate of potable water that can be obtained from the unit will impact the size of population that can feasibly be supported from this project.
- Cost – Water production as well as construction and maintenance is included in the overall cost. Keeping the overall cost as low as possible is a key factor for the success of the project.
